小孩理财
Title: Guide to Interest Rates for Children's Financial Planning
Introduction:
Teaching children about financial planning and the concept of interest rates is an excellent way to educate them about money management and encourage responsible financial habits. In this article, we will discuss the different aspects of interest rates for children's financial planning and provide practical guidance for parents or guardians.
Understanding Interest Rates:
1. What are interest rates?
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money or the return earned on savings or investments.
They are typically expressed as a percentage of the principal amount.
2. Importance of teaching children about interest rates:
Understanding interest rates helps children grasp the value of saving, budgeting, and making informed financial decisions.
It promotes longterm financial planning and fosters financial independence in adulthood.
Different Types of Interests Rates:
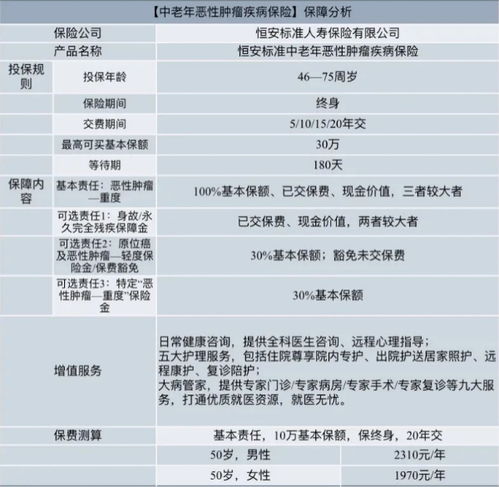
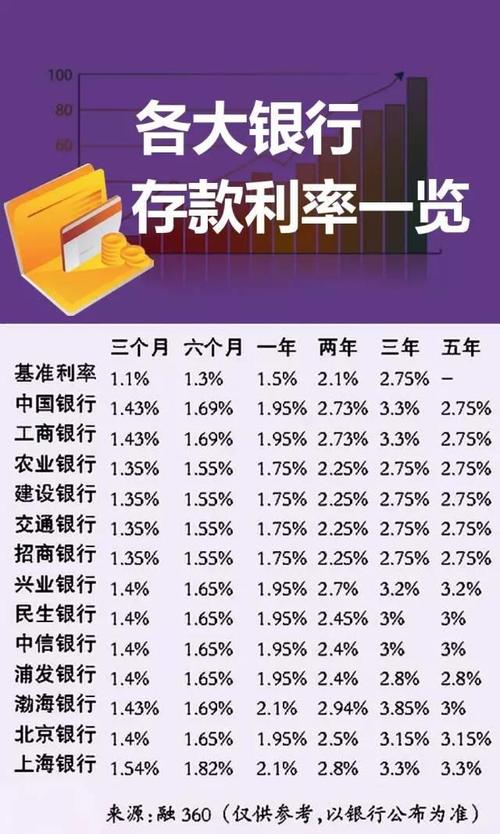
1. Saving Account Interest Rates:
Children can open savings accounts specifically designed for minors.
These accounts usually offer a lower interest rate, typically around 0.5% 2.5%, to encourage regular savings habits.
2. Fixed Deposit Interest Rates:
Fixed deposits are another option for children's investments.
The interest rates offered on fixed deposits vary among banks but generally range from 4% 7%.
Longerterm deposits tend to offer higher interest rates.
3. Education Savings Plan Interest Rates:
Education savings plans, such as 529 plans in the United States, offer tax advantages specifically for educational expenses.
The interest rates depend on the investment options chosen within the plan.
Rates can vary and are influenced by the performance of the underlying investments.
Teaching Strategies and Recommendations:
1. Start with the basics:
Introduce the concept of interest rates at an ageappropriate level, using simple language and reallife examples.
Discuss the benefits and potential risks that come with borrowing or lending money.
2. Promote saving habits:
Encourage children to save money regularly and monitor their savings account's interest growth.
Teach them how compound interest works and how consistent saving can lead to longterm financial gains.
3. Invest in financial literacy education:
Consider books, games, or online resources that teach children about financial management and interest rates.
Engage in discussions about financial topics and encourage questions and curiosity.
4. Explore investment options together:
As children get older, introduce investment opportunities like fixed deposits or education savings plans.
Educate them about the risks and potential returns associated with different investment choices.
Conclusion:
Teaching children about interest rates is an essential element of their financial education. By understanding the concept of interest rates and implementing saving and investing strategies, children can develop responsible financial habits and set themselves up for future financial success. Encourage open conversations about finance, guide them in making informed decisions, and equip them with the knowledge to handle their finances wisely.