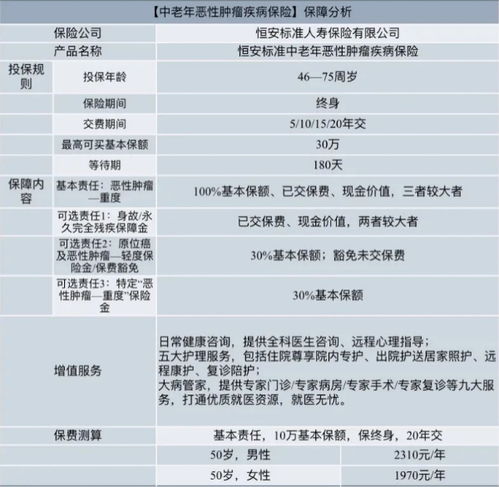
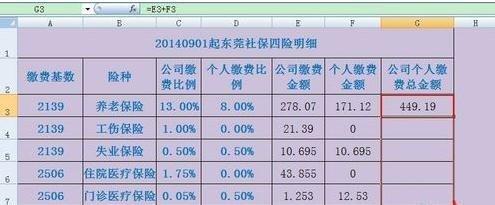
养老保险基本工资怎么计算
Title: Understanding Insurance Compensation Structures
In the insurance industry, compensation can vary widely depending on factors such as job role, experience level, performance, and the specific company's policies. Let's delve into the typical components and calculation methods for insurance industry compensation.
1. Base Salary:
The base salary forms the foundation of an insurance professional's compensation. It's typically determined by factors such as the individual's level of education, experience, and the prevailing market rates for similar roles. Base salaries can vary significantly across different roles within the insurance industry, ranging from entrylevel positions to senior management roles.
2. Commission:
Many insurance roles, particularly those in sales and brokerage, include a commission component. This commission is often calculated based on the premiums generated by the insurance policies sold by the individual. The commission rate can vary depending on the type of insurance (e.g., life insurance, property insurance, health insurance) and the specific agreements between the individual and the insurance company or brokerage firm.
3. Bonuses:
Bonuses are another common form of compensation in the insurance industry and are often tied to individual and/or company performance metrics. For example, an insurance agent may receive a bonus for exceeding sales targets, while an underwriter may receive a bonus based on the profitability of the insurance policies they have assessed. Bonuses can be discretionary or structured as part of a formal incentive program.
4. Renewal Commissions:
In certain insurance roles, such as those in life insurance or certain types of property and casualty insurance, professionals may receive renewal commissions. These commissions are paid when policyholders renew their insurance policies, providing ongoing income for the individual who originally sold or underwrote the policy.
5. Profit Sharing:
Some insurance companies offer profitsharing arrangements as part of their compensation packages. This typically involves sharing a portion of the company's profits with employees based on predetermined criteria such as tenure, job level, or individual performance.
6. Overrides:
Overrides are additional commissions or bonuses paid to individuals who manage teams of insurance professionals. These overrides are typically calculated based on the performance of the team members, incentivizing team leaders to support and mentor their colleagues to achieve collective goals.
Calculation Example:
Let's consider a hypothetical scenario of an insurance sales agent:
Base Salary: $50,000 per year
Commission Rate: 10% of premiums generated
Annual Premiums Generated: $500,000
Bonus: $5,000 for meeting sales targets
Calculation:
Commission Earned: $500,000 * 10% = $50,000
Total Compensation: Base Salary Commission Bonus = $50,000 $50,000 $5,000 = $105,000
Conclusion:
In summary, insurance industry compensation typically consists of a combination of base salary, commission, bonuses, renewal commissions, profitsharing, and overrides. The specific mix and calculation methods vary depending on factors such as job role, performance, and company policies. Understanding these components is essential for both insurance professionals seeking to maximize their earnings potential and employers aiming to attract and retain top talent in the industry.
For more detailed information on compensation structures within specific roles or companies, individuals should consult their employers' human resources departments or relevant industry resources.